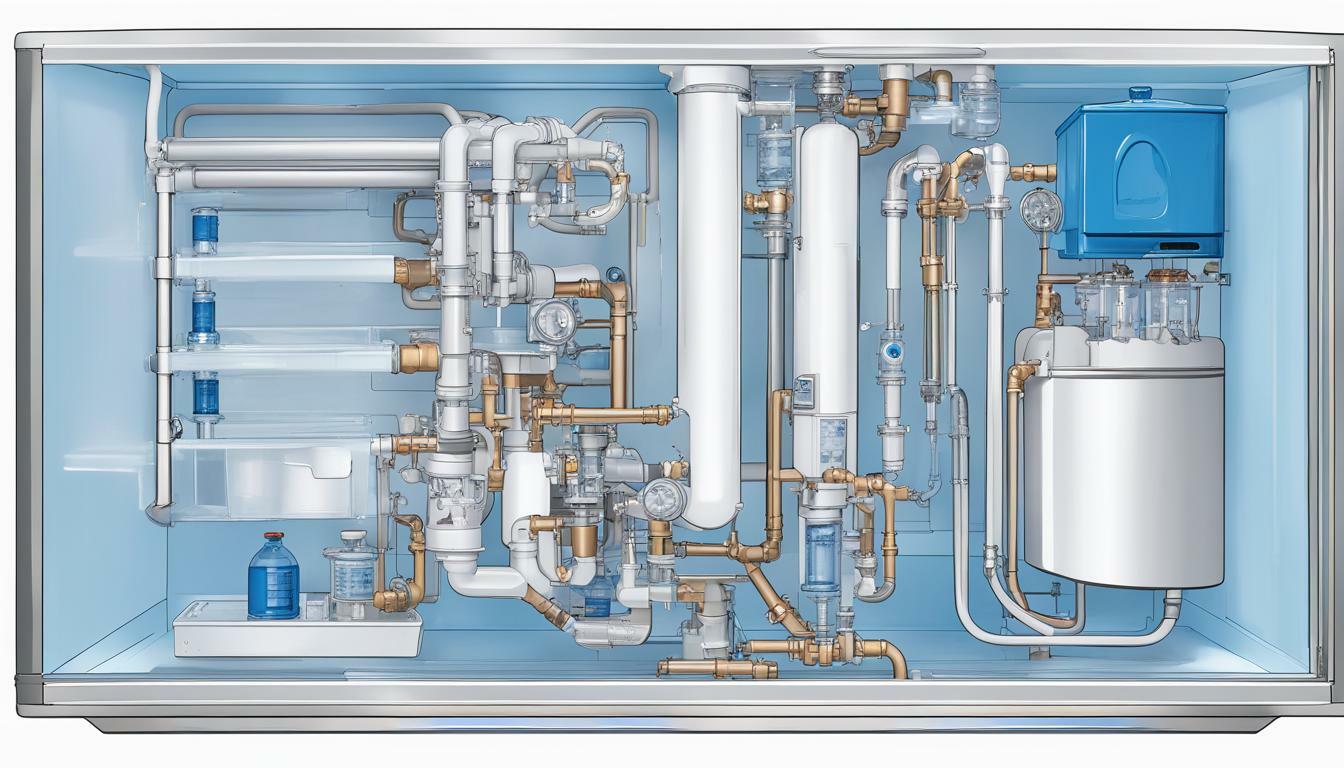
If you’ve ever wondered how your drinks get chilled so quickly, you can thank the technology behind ice maker machines. These machines work by taking in water, freezing it, and forming it into ice before dispensing it into a storage bin.
Understanding the inner workings of an ice maker machine unveils the fascinating process behind something we often take for granted – the creation of ice. Ice is ubiquitous and essential in modern life, from cooling beverages to preserving food. Yet, few of us pause to consider the intricate mechanism that transforms water into the frozen cubes we rely on.
This exploration delves into the fundamental principles and understanding of the process of how ice maker machines work, shedding light on the science and engineering that make this everyday convenience possible. Whether you’re a curious enthusiast or want to appreciate the technology, this journey into ice-making mechanics promises to be enlightening and refreshingly cool. Let’s take a closer look at the mechanism and operation of ice maker machines.
Key Takeaways:
- Ice maker machines take in water, freeze it, and form it into ice before storage.
- The mechanism behind ice maker machines involves several components and technologies.
- Understanding the process and components involved in ice maker machines can help in their maintenance and troubleshooting.
Ice Maker Machine Components
An ice maker machine has several crucial components working together to produce ice. Understanding these components is critical to understanding how the machine works.
| Component | Function |
| Compressor | Compresses the refrigerant gas, raising its temperature and pressure. |
| Condenser | Transfers heat from the refrigerant gas to the surrounding air or water, causing the gas to cool and condense into a liquid. |
| Evaporator | Facilitates the heat exchange process by absorbing heat from the surrounding air or water, causing the refrigerant liquid to evaporate and become a gas again. |
| Water Valve | Controls the flow of water into the ice maker machine. |
These components work harmoniously to create the cooling effect required to freeze water and create ice. Other components of an ice-maker machine include a motor, a thermostat, and a timer to regulate the ice-making process.
Advancements in ice maker machine technology have allowed for the creation of more energy-efficient and environmentally friendly machines.
A better understanding of these components can assist in choosing the best ice maker machine for a given situation. If you want to know about the Della water machine, we have the article” How Long Does a Della Water Machine Ice Maker Take to Make Ice the First Time?“
Ice Maker Machine Process
The ice maker machine process involves several steps to produce and store ice. Understanding how these steps work is essential to maintaining and optimizing the performance of an ice maker machine.
Step 1: Water Intake
The first step in the ice maker machine process is water intake. The sensor detects the water level in the machine and regulates the water valve to draw water into the machine.
Once the water reaches the correct level, the valve shuts off, and the freezing process begins.
Step 2: Freezing
The compressor initiates the freezing process, facilitating refrigerant cooling and directing it towards the evaporator. The evaporator releases the cooling energy into the water, causing it to freeze into ice cubes. Ice begins forming on the surface of the evaporator and continues to grow until it forms a complete cube, which the machine then releases into the storage bin.
Step 3: Harvesting
Once the ice cubes have formed, the harvesting process begins. A heating element warms the evaporator’s surface, causing the ice to melt slightly and release from the surface. The ice is then collected by a harvesting mechanism and released into the ice storage bin.
Step 4: Storage
The ice is stored in the ice storage bin until it is needed. The bin is kept at a constant temperature to prevent the ice from melting and ensure that it remains frozen. A sensor inside the bin detects the ice level and signals the ice maker machine to start the water intake process when the ice level is low.
By understanding the ice maker machine process, you can properly maintain and troubleshoot the machine’s components and ensure optimal performance. Regular cleaning and maintenance will help prevent common issues and extend the machine’s lifespan.
Water Supply and Intake
One of the critical elements of the ice maker machine operation is the water supply and intake mechanism. It ensures a steady water flow into the machine, frozen to make ice.
The water supply typically comes from a building’s main water line, connected to the ice maker machine through a designated water inlet valve. When the machine needs water, the valve opens, allowing water to flow through a plastic tube and into the machine. The water then fills the ice mold and freezes into ice cubes over time.
The water valve is a critical component of the ice maker machine mechanism, as it controls water flow into the machine. Most modern ice maker machines use a solenoid valve, an electromagnetic component that can open and close the valve as needed.
In some cases, users may need to manually turn the water supply on and off to ensure the machine’s proper functioning. Additionally, installing a filter on the water line may be necessary to remove any impurities affecting the ice cubes’ taste and clarity.
Freezing and Ice Formation
Once the ice maker machine releases the water, it begins freezing. The refrigerant circulating through the machine cools the evaporator plate, and the water flows over it.
As the water makes contact with the evaporator plate, it begins to freeze. The refrigerant absorbs the heat from the water and carries it away, lowering the temperature of the evaporator below freezing point. It causes the water to freeze into a thin layer of ice on the evaporator plate.
| Ice Formation | The layer of ice on the evaporator plate continues to grow as more water is released and freezes. The thickness of the ice is controlled by a thermostat that monitors the temperature of the evaporator plate. |
| Circulation | The refrigerant continues to circulate through the machine, removing the heat from the evaporator plate. This causes the ice to remain frozen and prevents it from melting. |
As the ice layer grows thicker, the ice maker machine detects when it has reached the desired thickness, triggering the next step in the process: harvesting and storage. The following section covers it in detail.
How does the refrigerant work?
Refrigerant is a substance that removes heat from the evaporator plate and keeps the ice frozen. It circulates through the machine in a closed-loop system, absorbing heat as it travels through the evaporator and releasing it through the condenser. The refrigerant can take on either a liquid or a gas form, depending on the temperature and pressure in the machine.
The refrigerant used in ice maker machines is typically a hydrofluorocarbon (HFC), known for its low toxicity and flammability. However, some ice maker machines may use other refrigerants with different environmental impacts. It is essential to research the specific refrigerant used in your ice maker machine and its potential environmental impact.
Harvesting and Storage
Once the ice has formed, the harvesting process begins. The first step is to stop the water flow into the ice maker machine. Then, the evaporator plate is heated up to loosen the ice from the plate. This technique usually occurs by employing a heating element or reversing the refrigeration cycle, inducing an increase in temperature within the evaporator.
Next, a harvesting mechanism removes the ice from the plate. Most commercial ice maker machines use a rotating cylinder or harvesting fingers. The ice is then dropped into a storage bin or dispenser and kept until used.
| Storage Bins | Dispensers |
| The storage bin is insulated to keep the ice cold and prevent it from melting. It typically has a sliding door on the front that can be opened to access the ice. Some models also have a built-in ice crusher. | A dispenser is used to automatically dispense ice into cups or containers. Some dispensers have a motorized auger that moves the ice to the dispensing chute, while others rely on gravity to move the ice. |
The storage capacity of an ice maker machine depends on the size of the storage bin or dispenser. Commercial models can store hundreds of pounds of ice, while smaller homes may only store a few pounds.
Proper storage of the ice is crucial to maintain its quality and prevent contamination. Regularly clean the storage bin to remove any buildup of ice or debris.
It is also essential to monitor the temperature of the storage bin to ensure that the ice remains frozen and does not melt.
Maintenance and Cleaning
Proper maintenance and cleaning of your ice maker machine is crucial to ensure its optimal performance and longevity. With these tips and rules, your machine will run well, and you won’t have to pay for expensive fixes or replacements.
Regular Cleaning
One of the most important things you can do to maintain your ice maker machine is regularly cleaning it. It would help if you cleaned it at least once every six months. Here’s how:
| Step | Description |
| Step 1 | Unplug the machine or turn off the power supply. |
| Step 2 | Empty the ice bin and discard any remaining ice. |
| Step 3 | Remove any removable parts, such as the ice tray, and wash them with warm, soapy water. |
| Step 4 | Wipe down the interior of the machine with a damp cloth or sponge. Be sure to get into any nooks and crannies. |
| Step 5 | Run a cleaning cycle using a commercial ice machine cleaner according to the manufacturer’s instructions. |
| Step 6 | Rinse the machine thoroughly with clean water. |
| Step 7 | Replace the removable parts and turn on the power supply. |
It’s also a good idea to regularly check and clean the water inlet valve and the condenser coils to ensure they function correctly and are free from dirt and debris.
Professional Maintenance
In addition to routine maintenance, you must schedule periodic expert servicing for your ice maker equipment. A technician with the proper training can spot possible problems and make any repairs or maintenance needed to keep your machine running at its best.
Adhering to the manufacturer’s prescribed maintenance plan and using just authorized cleaners and components are imperative practices to prevent any potential harm to the equipment or the invalidation of the warranty.
Following these tips and guidelines ensures that your ice maker machine operates effectively and efficiently for years.
Common Issues and Troubleshooting
While ice maker machines are generally reliable, they can sometimes encounter issues. Here are some of the most common problems and how to troubleshoot them:
The ice maker is not making ice.
Suppose the ice maker fails to produce ice. In that case, it is advisable to initially verify the proper connection of the appliance to a power source and ensure that the water supply valve is in the open position. If these are not the issue, it may be a problem with the motor or the water inlet valve. Consult the manufacturer’s instructions for further troubleshooting steps.
Ice maker produces small or misshapen ice cubes.
It could be a sign of low water pressure or an issue with the water filter. Check that the water pressure is at the recommended level and replace the filter if necessary.
What to do if the ice maker is producing too much ice?
Ensure you have set the correct ice cube size on the ice maker and that the ice bucket is filling appropriately.
If the problem persists, there may be an issue with the control module or thermostat.
Ice has a strange odor or taste.
It could be due to a dirty water filter or mineral buildup in the ice maker. Make sure to clean and replace the water filter regularly. To effectively clean the ice maker, we recommend creating a solution consisting of equal water and vinegar. Run this solution through a complete cycle within the ice maker. Afterward, it’s advisable to run a separate cycle using plain water to ensure the removal of any residual solution.
The ice maker is making loud noises.
If your ice maker produces loud or unusual noises, it may result from a faulty fan, motor, or compressor. Turn off the ice maker and consult the manufacturer’s instructions for further troubleshooting and repair steps.
By following these troubleshooting steps, you can keep your ice maker machine running smoothly and ensure a steady supply of ice for your needs.
Energy Efficiency and Environmental Impact
Ice maker machines have come a long way regarding energy efficiency and minimizing environmental impact. With technological advancements, manufacturers have developed models that consume significantly less electricity and water than older models. These machines use innovative technology to produce more ice with less energy input, making them a cost-effective and eco-friendly choice for businesses and households.
One technology that has contributed to improved energy efficiency is high-performance compressors that consume less energy while producing faster cooling. The design of the condenser coils has also aimed to improve heat transfer, thereby reducing power consumption.
Additionally, some models now use eco-friendly refrigerants with lower global warming potentials, reducing environmental impact. The size of an ice maker machine is an additional component that influences its energy efficiency.
Generally, larger machines consume more power than smaller ones. Therefore, to minimize your environmental impact, choose a machine of the appropriate size for your needs. An oversized machine will consume more energy and produce more ice than you require, wasting energy and water.
Furthermore, it’s worth noting that some ice maker machines now have sensors that automatically turn off the machine when the ice bin is full, preventing energy waste. Other machines have timers that you can adjust according to your usage patterns, allowing you to save energy during off-peak hours.
In summary, when choosing an ice maker machine, consider the technology used to minimize energy consumption and water waste and the appropriate size for your needs. Individuals can minimize their carbon footprint by making intelligent choices while enjoying the advantages of ice production at their convenience.
Conclusion
Understanding how ice maker machines work is essential for anyone who relies on them to produce ice. By familiarizing yourself with the various components, processes, and mechanisms involved in their operation, you can better appreciate the technology behind these machines and ensure their optimal performance and longevity.
Remember to pay attention to the water supply and intake mechanisms, the freezing and ice formation process, the harvesting and storage mechanism, and the importance of regular maintenance and cleaning. Additionally, be mindful of common issues that may arise and how to troubleshoot them effectively.
As technological advancements continue, ice maker machines become increasingly energy-efficient and environmentally friendly. Investing in a high-quality machine and staying informed about the latest developments allows you to enjoy all the benefits of ice production without compromising sustainability.
FAQ
Q: How does an ice maker machine work?
A: An ice maker machine follows a step-by-step process involving various components and technologies. It starts with the water supply and intake mechanism, where the water valve controls water flow into the ice maker machine. The water pump then moves into the evaporator, where a refrigerant cools it. The cooling causes ice to form on the surface of the evaporator. When the ice forms, the ice maker starts picking the ice out of the evaporator and putting it in a particular storage bin. This process will keep going until enough ice is built.
Q: What are the components of an ice maker machine?
A: An ice maker machine has several components, including a compressor, condenser, evaporator, and water valve. The compressor is in charge of the compression of the refrigerant, resulting in an elevation of both its temperature and pressure.
The condenser then cools the refrigerant, causing it to condense back into a liquid state. Pump the cooled refrigerant into the evaporator, where ice formation occurs. Finally, the water valve controls water intake into the ice maker machine.
Q: What is the process involved in an ice maker machine?
A: An ice maker machine begins with the water supply and intake mechanism, where the water valve allows water to enter the machine. A refrigerant flowing through it cools the water, and the pump moves it into the evaporator. As the water freezes, ice forms on the surface of the evaporator. Once the ice is formed, the ice maker machine actively initiates the harvesting process, removes the ice from the evaporator, and stores it in a designated storage bin. This active process continues until the desired amount of ice is produced.
Q: How does the water supply and intake mechanism work?
A: The water valve regulates an ice maker machine’s water supply and intake mechanism. When the ice maker machine is ready to produce ice, it actively opens the water valve, enabling water to flow into the machine. The water valve controls the water flow, supplying the correct amount to the ice maker machine. Once inside the machine, it is pumped into the evaporator to initiate ice-making.
Q: How do freezing and ice formation occur in an ice maker machine?
A: Freezing and ice formation in an ice maker machine occur inside the evaporator. The evaporator is cooled by a refrigerant flowing through it, causing the temperature of the evaporator to drop. When water enters the evaporator, the cold surface causes the water to freeze and form ice. This process continues until the ice covers the entire surface of the evaporator. Once the ice is fully formed, the ice maker machine starts harvesting to remove the ice from the evaporator.
Q: How does an ice maker machine harvest and store ice?
A: An ice maker machine harvests and stores ice through several mechanisms. Once the ice is entirely formed on the evaporator, the ice maker machine activates a harvesting process. This process involves heating the evaporator slightly to release the ice from its surface. The ice then falls into a designated storage bin, where it is stored until needed. The storage bin is designed to keep the ice cold and prevent it from melting. When the ice supply runs low, the ice maker machine will start the process again to produce more ice.
Q: How should I maintain and clean my ice maker machine?
A: Proper maintenance and cleaning are crucial for an ice maker machine’s optimal performance and longevity. We recommend regularly cleaning the ice maker machine, including the water valve, evaporator, and storage bin, following the manufacturer’s instructions and using appropriate cleaning solutions. It is also essential to check and replace worn-out or damaged components, such as filters or seals, to ensure smooth operation. Regular maintenance and cleaning will help prevent issues and maintain the quality of the ice produced.
Q: What are some common issues with ice maker machines, and how can they be resolved?
A: Some common issues with ice maker machines include low ice production, ice cubes that are too small or misshapen, and unusual noises. Most of the time, we can solve these problems by checking the water source and intake system to ensure enough water flow. It’s also a good idea to check and clean the evaporator and condenser to eliminate any dirt or blockages that could stop the machine from making ice. If the problems keep happening, it’s best to look at the manufacturer’s troubleshooting guide or get help from an expert.
Q: How do ice maker machines contribute to energy efficiency and environmental impact?
A: Ice maker machines have undergone technical developments to enhance energy efficiency and reduce their environmental footprint. Manufacturers have developed energy-efficient models that reduce energy consumption while maintaining optimal ice production. Some ice maker machines have also incorporated water-saving features to minimize water waste. These advancements aim to reduce the carbon footprint associated with ice production and promote sustainable practices in the food service industry.
Joanne Evans, a seasoned expert in the ice maker industry, brings a wealth of knowledge on cooling solutions. With a passion for innovation, she guides readers through the frozen frontier, sharing insights on the best ice makers for every need.